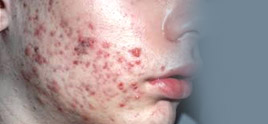
Acne vulgaris is one of the most common dermatologic disorders encountered in everyday clinical practice. It is a disease of the sebaceous follicle, primarily the pilosebaceous units located on the face, chest, and back. Inflammatory and non- inflammatory lesions presents with highly variable morphologies.
Specific Investigations
None are required routinely.
- Consider microbiology to exclude Gram- positive or- negative folliculitis
- Consider endocrine work-up if hyperandrogenemia is suspected
Therapy
Comedonal Acne
- Topical retinoids
Mild Papulopustular Acne
- Benzoyl peroxide (topical) with topical retinoids or with topical antimicrobials ( antibiotics or azelaic acid)
Moderate Populopustular Acne Without Scarring
- Benzoyl peroxide ( topical) with topical retinoids and topical antibiotics
Moderate Populopustular Acne With Light Scarring
- For males use oral antibiotics ( tetracyclines, macrolieds) with benzoyl peroxide (topical) or topical retinoids
- For femals use an oral anti- androgen contraceptive with benzoyl peroxide (topical) and topical antibiotics
Severe Populopustular Acne
- Oral isotretioin
Nodulocystic and / or Conglobate Acne
- Oral isotretioin
Acne Fluminans
- Oral isotretioin with low-dose oral corticosteroids