+91 999-080-4085 drsandeshg@rediffmail.com
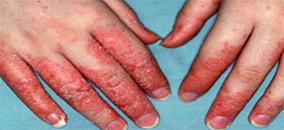 Eczema refers to the inflammation or irritation of the outer layer of the skin (epidermis). It causes skin dryness or recurring skin rashes. It is a way of skin’s reaction to a source of allergy or infection.
Eczema refers to the inflammation or irritation of the outer layer of the skin (epidermis). It causes skin dryness or recurring skin rashes. It is a way of skin’s reaction to a source of allergy or infection.
Symptoms may range from redness, swelling, itching, crusting, cracks to the bleeding of the skin. Eczema is non-contagious and particularly common among housewives and young children.
Though the exact cause of eczema is unknown, it is linked to an overactive response in the body's immune system to certain triggers. People with a history of other allergies or asthma are more prone to develop eczema.
While eczema itself cannot be prevented, outbreaks can usually be avoided or the severity reduced by practicing simple guidelines. Patients are advised to abide by the following:
Though there is no permanent cure for eczema, but proper treatment from dermatologist generally controls the disease. Treatment for eczema aims to relieve and prevent itching, which can lead to infection. Because dry skin often makes skin itchy, applying moisturizer after bathing when skin is damp is recommended. Other treatment options include:
Medication: For mild eczema creams and ointments are often prescribed to reduce inflammation. When the affected area becomes infected, antibiotics may be necessary to kill the infection-causing bacteria. For severe cases, oral medication is necessary to reduce the symptoms and spread of the disease.
Call us at +91-9990804085, +91-9990804089 | Email at drsandeshg@rediffmail.com